- https://blog.csdn.net/mayuming77/article/details/77988637
- 我们想法:
- 能不能将多个硬盘,映射成一个逻辑的硬盘,那样我们程序就不用关心复杂的地址问题了,也不用关系是哪个device了? DM-raid技术RAID全称为独立磁盘冗余阵列(Redundant Array of Independent Disks)
- 将某个地址段的数据进行加密,只有授权方式才可访问,比如FDE。 DM-crypt技术
- 访问存储介质上的数据时,校验下是否被篡改过。DM-verity技术。
总结一下:DM就是Device-Mapper的缩写,也就说上述的想法都可以基于Device Mapper实现,Device Mapper可不仅仅实现了这些,还包括LVM2、DM-multipach等。
- 什么是Device Mapper?
- Device Mapper是 Linux 2.6内核中提供的一种将物理块设备的映射虚拟(逻辑)块设备的框架机制,在该机制下,开发者可以很方便的根据自己的需要制定实现存储资源的管理策略,比如过滤、IO重定向、dm-verity这种hash tree的校验、raid多个磁盘管理等。
- Device Mapper在内核中是以一个块设备注册的。映射到Device Mapper框架上的物理设备,通过映射时所选择的方式进行IO处理。
- Device mapper本质功能就是根据映射关系和target driver描述的IO处理规则,将IO请求从逻辑设备mapped device转发相应的target device上。
举例:我将system分区以dm-verity target方式映射到devicemapper上,当用户程序访问system数据时,要通过device mapper的规则后才能转发到system分区上。 Device Mapper处于LinuxStorage Stack位置: 

简单点:  
Device Mapper在内核中的体系架构: 
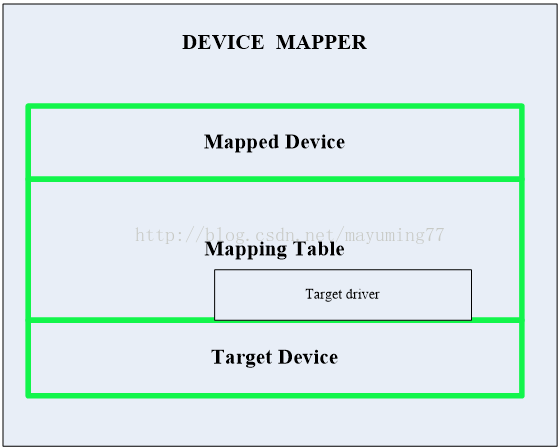
从上图就可以看出,Device Mapper有三部分组成,分别有Mapped Device、Mapping Table、Target Device,说此图的时候必须说一下内核设计的哲学,内核设计经常将一个框架实现,给用户态提供尽量少、简单接口来下发策略,内核根据用户态下发策略运行相应机制。Device Mapper机制也不例外: Mapped Device:又称MD,注意不是DM,MD是一个逻辑的抽象设备,用户态可以通过IOCTL访问操作,它通过Mapping Table描述的映射关系与Target Device建立映射关系。 Mapping Table:描述了Target Device和Mapped Device的映射关系,其中最核心的是其指定了这种映射关系使用了何种Target Driver。 Target Driver:其实严格的说,这不是Device Mapper框架的一部分,因为Target Driver以插件的方式插入Device Mapper的统一框架定义的一组接口上,允许开发者根据实际的需要定制自己的IO处理规则,Device Mapper目前支持的Target Driver有linear,raid,verity,mulipath,snapshot,mirror,crypt,cache,era,thin等。 Target Device:目标设备,Target device 表示的是 mapped device所映射的物理空间段,对 mapped device所表示的逻辑设备来说,就是该逻辑设备映射到的一个物理设备。
Device mapper中这三个对象和 target driver插件一起构成了一个可迭代的设备树。在该树型结构中的顶层根节点是最终作为逻辑设备向外提供的 mapped device,叶子节点是 target device 所表示的底层物理设备,Device-Mapper的映射模型: 单一型:单个 mapped device和 target device组成,每个target device都是被mapped device独占的,只能被一个 mapped device使用 
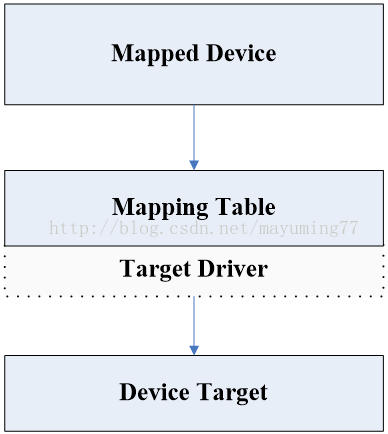 一对多型:多个 target device映射到一个Mapped device上。 
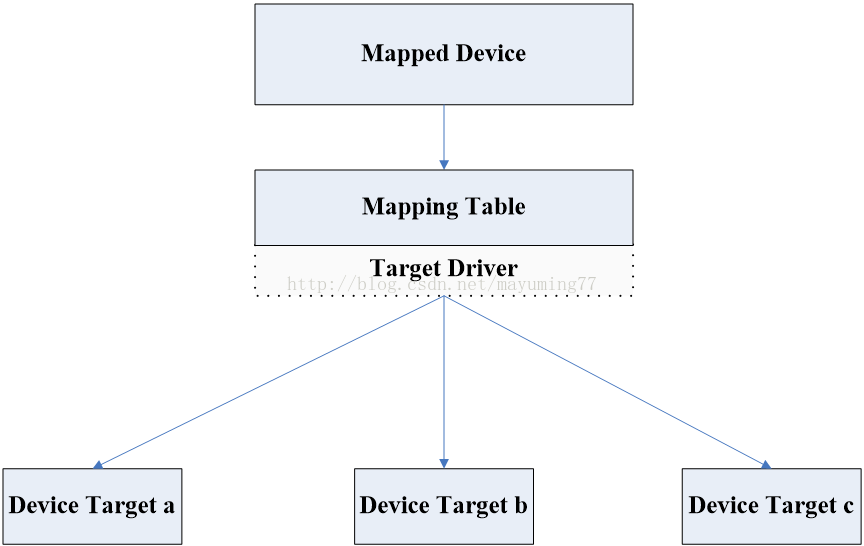 组合型:一个 mapped device又可以作为它上层 mapped device的 target device被使用,该层次在理论上可以在 device mapper 架构下无限迭代下去。 
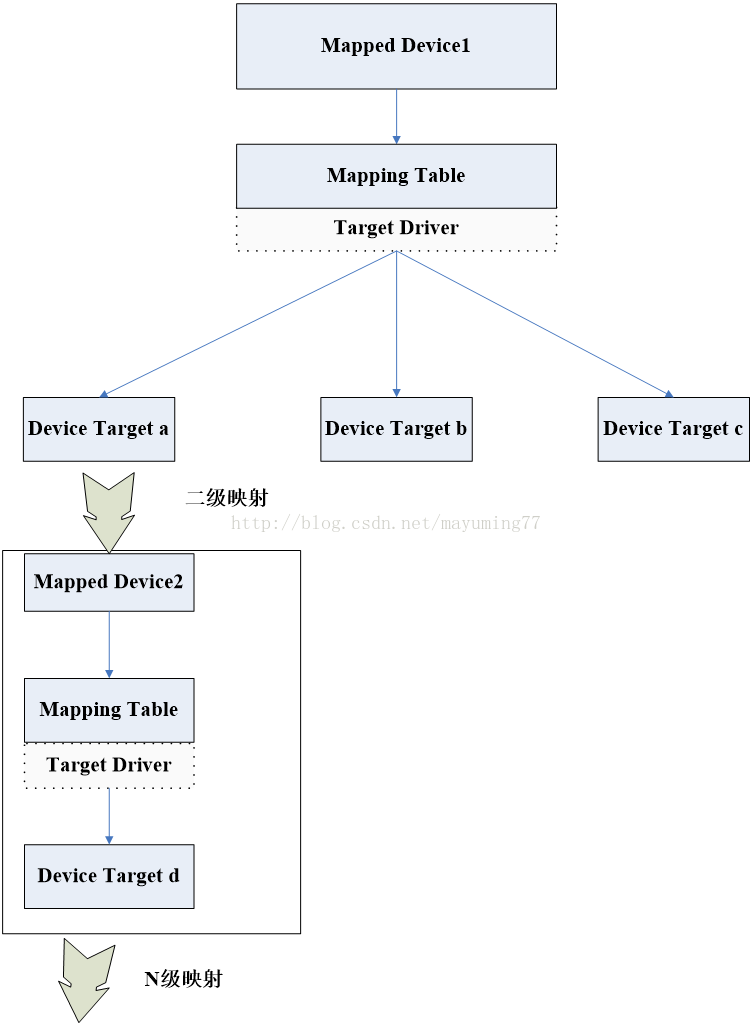 总结一下: 一个Device Target只能映射到一个Mapped Device,不可以映射到两个或多个Mapped Device,如果不这样,那么当访问这个Device Target时,DeviceMapper框架不知道选择哪个Mapped Device,这样将系统很纠结,系统表示做不到。 ,可以多个Device Target映射一个MappedDevice上,你访问多个不同Device Target数据时,需要经过Mapped Device相同的IO策略,Device Mapper框架表示我不纠结,可以很好的处理,我按照你的映射关系可以找到你就可以。 逻辑设备也可以映射到Mapped Device上。DeviceMapper表示我看到的都是映射关系,映射表让我怎么处理我就怎么处理,不管你是逻辑设备还是真实的物理设备。
在Kernel目录下Documentation/device-mapper找到Device-Mapper相关文档。 在kernel目录下drivers/md/找到相关实现的code。
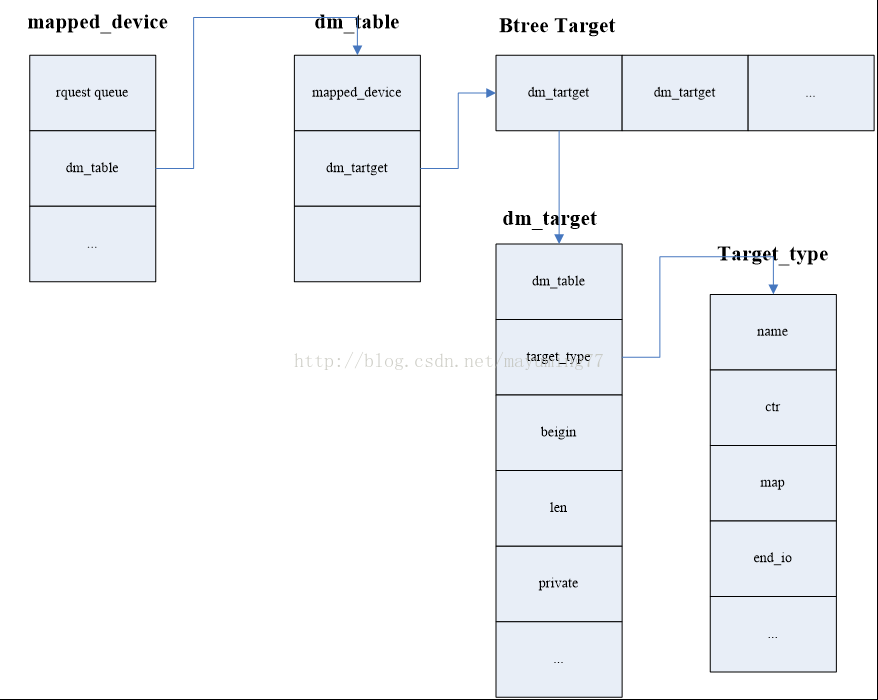
主要的数据结构, mapped_device是Mapped device抽象一个device。 struct mapped_device { struct srcu_struct io_barrier; //SRCU:http://www.wowotech.net/kernel_s ... inux2-6-23-RCU.html struct mutexsuspend_lock; atomic_t holders; atomic_t open_count;
/* * The currentmapping. * Usedm_get_live_table{_fast} or take suspend_lock for * dereference. */ struct dm_table *map; //Mapping Table
struct list_headtable_devices; struct mutextable_devices_lock;
unsigned long flags;
struct request_queue*queue; unsigned type; //Type of table and mapped_device's mempool /* Protect queue andtype against concurrent access. */ struct mutextype_lock;
struct target_type*immutable_target_type;
struct gendisk *disk; char name[16];
void *interface_ptr;
/* * A list of ios thatarrived while we were suspended. */ atomic_t pending[2]; wait_queue_head_twait; struct work_structwork; struct bio_listdeferred; spinlock_tdeferred_lock;
/* * Processing queue(flush) */ structworkqueue_struct *wq;
/* * io objects areallocated from here. */ mempool_t *io_pool;
struct bio_set *bs;
/* * Event handling. */ atomic_t event_nr; wait_queue_head_teventq; atomic_t uevent_seq; struct list_headuevent_list; spinlock_tuevent_lock; /* Protect access to uevent_list */
/* * freeze/thawsupport require holding onto a super block */ struct super_block*frozen_sb; struct block_device*bdev;
/* forced geometrysettings */ struct hd_geometrygeometry;
/* kobject andcompletion */ structdm_kobject_holder kobj_holder;
/* zero-length flushthat will be cloned and submitted to targets */ struct bio flush_bio;
struct dm_statsstats; };
dm_table 是Device Mapper中的MappingTable的抽象。 struct dm_table { struct mapped_device *md; unsigned type;
/* btree table */ unsigned int depth; unsigned intcounts[MAX_DEPTH]; /* in nodes */ sector_t*index[MAX_DEPTH];
unsigned intnum_targets; unsigned intnum_allocated; sector_t *highs; struct dm_target *targets;
struct target_type*immutable_target_type; unsignedintegrity_supported:1; unsigned singleton:1;
/* * Indicates the rwpermissions for the new logical * device. This should be a combination of FMODE_READ * and FMODE_WRITE. */ fmode_t mode;
/* a list of devicesused by this table */ struct list_headdevices;
/* events get handedup using this callback */ void (*event_fn)(void*); void *event_context;
struct dm_md_mempools*mempools;
struct list_headtarget_callbacks; };
dm_target结构具体描述了 mapped_device和某个 target device的映射关系,Dm_target结构具体记录该结构对应 target device所映射的 mapped device逻辑区域的开始地址和范围,同时还包含指向具体 target device相关操作的 target_type结构的指针,而在dm_table结构中将这些 dm_target按照 B树的方式组织起来方便 IO请求映射时的查找操作 struct dm_target { struct dm_table*table; struct target_type *type; //开发者可以定制的device target部分
/* target limits */ sector_t begin; sector_t len;
/* If non-zero,maximum size of I/O submitted to a target. */ uint32_t max_io_len;
/* * A number ofzero-length barrier bios that will be submitted * to the target forthe purpose of flushing cache. * * The bio number canbe accessed with dm_bio_get_target_bio_nr. * It is aresponsibility of the target driver to remap these bios * to the realunderlying devices. */ unsignednum_flush_bios;
/* * The number ofdiscard bios that will be submitted to the target. * The bio number canbe accessed with dm_bio_get_target_bio_nr. */ unsignednum_discard_bios;
/* * The number ofWRITE SAME bios that will be submitted to the target. * The bio number canbe accessed with dm_bio_get_target_bio_nr. */ unsignednum_write_same_bios;
/* * The minimum numberof extra bytes allocated in each bio for the * target touse. dm_per_bio_data returns the datalocation. */ unsignedper_bio_data_size;
/* * If defined, thisfunction is called to find out how many * duplicate biosshould be sent to the target when writing * data. */ dm_num_write_bios_fnnum_write_bios;
/* target specificdata */ void *private; //表示具体的target device的域是dm_target中的private域
/* Used to provide anerror string from the ctr */ char *error;
/* * Set if this targetneeds to receive flushes regardless of * whether or not itsunderlying devices have support. */ boolflush_supported:1;
/* * Set if this targetneeds to receive discards regardless of * whether or not itsunderlying devices have support. */ booldiscards_supported:1;
/* * Set if the targetrequired discard bios to be split * on max_io_lenboundary. */ boolsplit_discard_bios:1;
/* * Set if this targetdoes not return zeroes on discarded blocks. */ booldiscard_zeroes_data_unsupported:1; }; 开发者可以定制的device target部分,Target_type结构主要包含指向具体 target device相关操作,主要包含了 target device对应的 target driver插件的名字、定义的构建和删除该类型target device的方法、该类target device对应的IO请求重映射和结束IO的方法等: struct target_type { uint64_t features; const char *name; struct module*module; unsigned version[3]; dm_ctr_fn ctr; dm_dtr_fn dtr; dm_map_fn map; dm_map_request_fnmap_rq; dm_endio_fn end_io; dm_request_endio_fnrq_end_io; dm_presuspend_fnpresuspend; dm_postsuspend_fnpostsuspend; dm_preresume_fnpreresume; dm_resume_fn resume; dm_status_fn status; dm_message_fnmessage; dm_ioctl_fn ioctl; dm_merge_fn merge; dm_busy_fn busy; dm_iterate_devices_fniterate_devices; dm_io_hints_fnio_hints;
/* For internaldevice-mapper use. */ struct list_headlist; };
数据结构关系: 
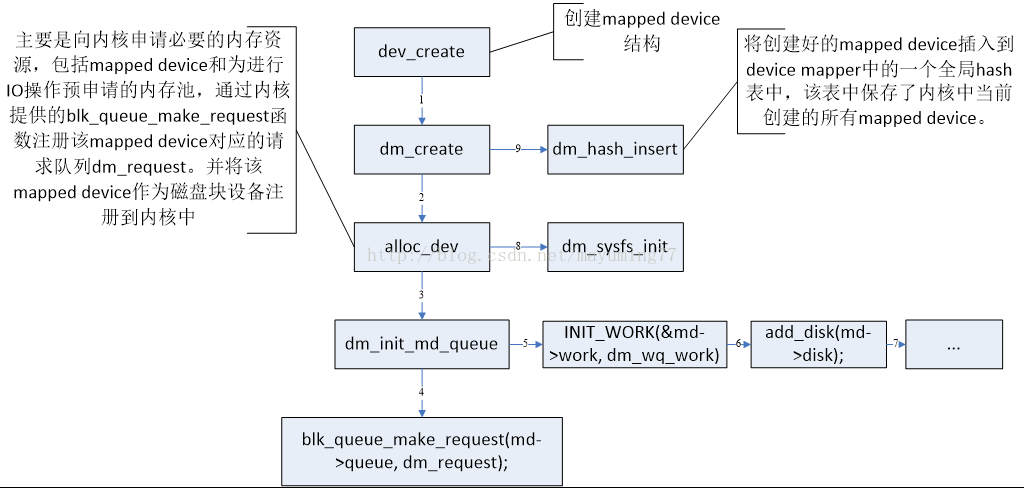
用户态fd =open("/dev/device-mapper", O_RDWR)),然后ioctl(fd, DM_DEV_CREATE, io)。 内核态根据ioctl命令调用dev_create函数创建相应的mapped device结构,dev_create主要做了以下几件事: 
用户态fd =open("/dev/device-mapper", O_RDWR)),然后ioctl(fd, DM_TABLE_LOAD, io)。 内核态根据ioctl命令调用table_load函数处理mapping table,table_load主要做了以下几件事: 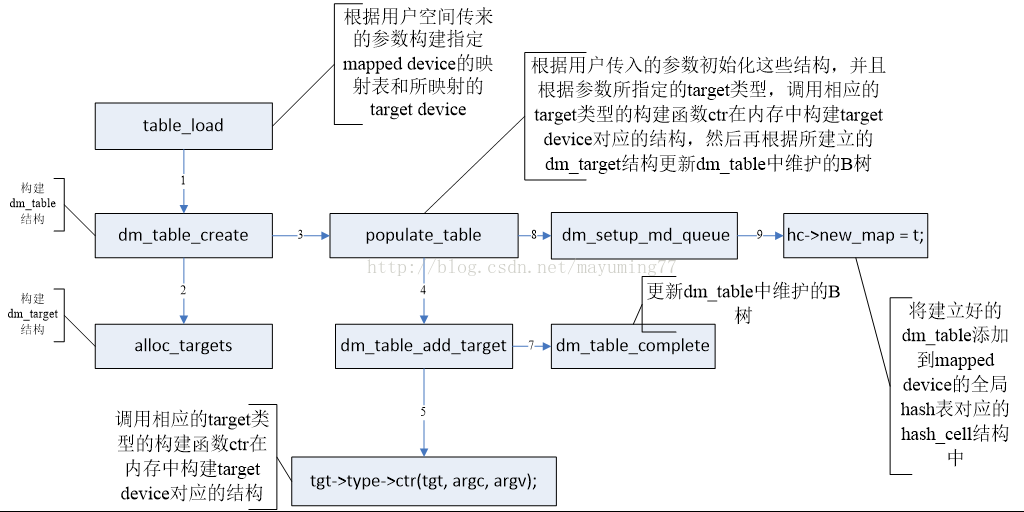 
用户态fd =open("/dev/device-mapper", O_RDWR)),然后ioctl(fd, DM_DEV_SUSPEND, io)。 内核态根据ioctl命令调用dev_suspend函数建立mappeddevice和映射表之间的绑定关系,dev_suspend主要做了以下几件事:
 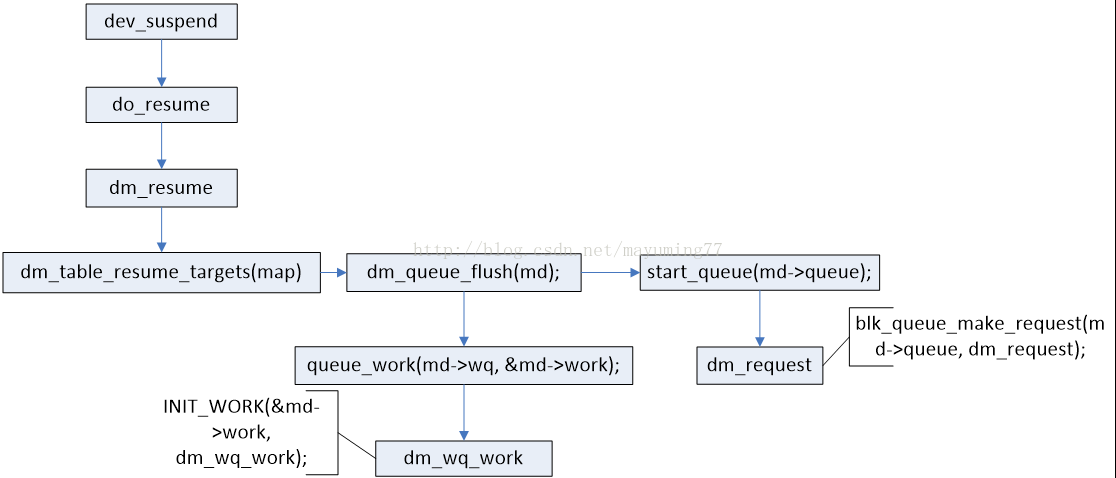
Device mapper本质功能就是根据映射关系和target driver描述的IO处理规则,将IO请求从逻辑设备mapped device转发相应的targetdevice上。dm_request实现这个机制  
至此,Device Mapper基础框架已经分析完毕。
|