|
详细理论可以自行百度补充 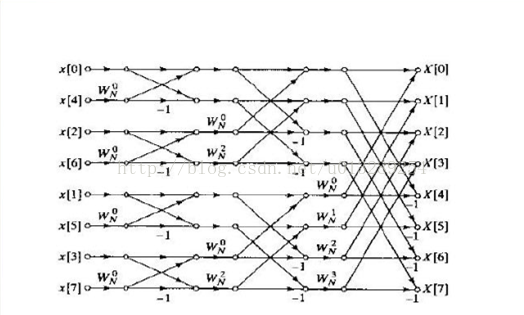
图1 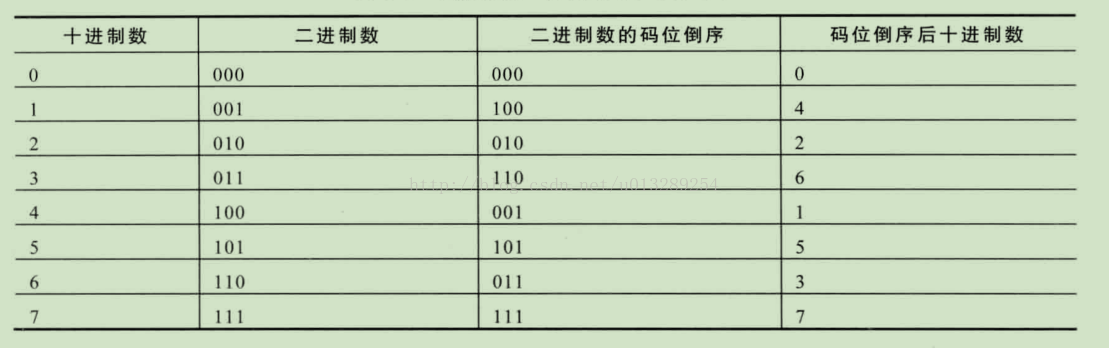
图2 为了方便处理数据,程序中会将图1中x[0],x[4],x[2]...x[7]进行倒序,也就是图2中的表。这里就直接上代码的。
for(j = 0; j< N; j++)
{
nInter = 0;
for(i = 0; i<k;i++)
{
if(j&(1<<i))//判断第i位是否为1 &两个结果为真的的才是真的 1&1 = 0 1%0 = 0
{
nInter += 1<<(k-i-1); //倒过去
}
}
real[j] = tempreal[nInter];
imag[j] = tempimag[nInter];
}
从图1中,我们可以看得出,FFT蝶形算法会使用三重循环,下一层的数据都是由上一层计算得到的。这里直接在代码里面备注一下,比较好解释的。
for(i = 0; i < k; i++)//第一重循环k=log2N,在这里N = 8,所以k = 2
{
step = 1<<(i + 1);
factor_step = N>>(i + 1);//旋转因数变化速度
//初始化旋转因子
factor_real = 1.0;
factor_imag = 0.0;
for(j = 0; j < step/2 ; j++)
{
for(k1=j;k1<N;k1+=step)
{
k2 = k1+step/2;//蝶形运算的两个输入
/*
temp_real = real[k1] + real[k2]*factor_real-imag[k2]*factor_imag;
real[k2] = real[k1] - (real[k2]*factor_real-imag[k2]*factor_imag);
real[k1]= temp_real;
temp_imag = imag[k1] + real[k2]*factor_imag+imag[k2]*factor_real;
imag[k2] = imag[k1] - (real[k2]*factor_imag+imag[k2]*factor_real);
imag[k1] = temp_imag;
*/
temp_real = real[k2]*factor_real-imag[k2]*factor_imag;
temp_imag = real[k2]*factor_imag+imag[k2]*factor_real;
real[k2] = real[k1]-temp_real;
imag[k2] = imag[k1]-temp_imag;
real[k1] = real[k1]+temp_real;
imag[k1] = imag[k1]+temp_imag;
}
factor_real = inv*cos(-2*PI*(j+1)*factor_step/N);
factor_imag = inv*sin(-2*PI*(j+1)*factor_step/N);
}
}
if(inv ==-1)
{
for(i = 0;i<=N-1;i++)
{
real=real/N;
imag=imag/N;
}
}
完整的代码可以见这里:
#include <iostream>
#include<math.h>
#define PI 3.1415926
using namespace std;
void fit(double real[],double imag[],int N,int k,int inv)
{
int i,j,k1,k2,m,step,factor_step;
double temp_real,temp_imag,factor_real,factor_imag;
if(inv!=1&&inv!=-1)
{
cout<<"FFT transformation require:inv=1"<<endl;
cout<<"FFT inverse transformation require:inv=-1"<<endl;
}
//倒序
double tempreal[8];
double tempimag[8];
for(i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
tempreal = real;
tempimag = imag;
}
int nInter = 0;
for(j = 0; j< N; j++)
{
nInter = 0;
for(i = 0; i<k;i++)
{
if(j&(1<<i))//判断第i位是否为1 &两个结果为真的的才是真的 1&1 = 0 1%0 = 0
{
nInter += 1<<(k-i-1);
}
}
real[j] = tempreal[nInter];
imag[j] = tempimag[nInter];
}
//蝶形算法
for(i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
step = 1<<(i + 1);
factor_step = N>>(i + 1);//旋转因数变化速度
//初始化旋转因子
factor_real = 1.0;
factor_imag = 0.0;
for(j = 0; j < step/2 ; j++)
{
for(k1=j;k1<N;k1+=step)
{
k2 = k1+step/2;//蝶形运算的两个输入
temp_real = real[k2]*factor_real-imag[k2]*factor_imag;
temp_imag = real[k2]*factor_imag+imag[k2]*factor_real;
real[k2] = real[k1]-temp_real;
imag[k2] = imag[k1]-temp_imag;
real[k1] = real[k1]+temp_real;
imag[k1] = imag[k1]+temp_imag;
}
factor_real = inv*cos(-2*PI*(j+1)*factor_step/N);
factor_imag = inv*sin(-2*PI*(j+1)*factor_step/N);
}
}
if(inv ==-1)
{
for(i = 0;i<=N-1;i++)
{
real=real/N;
imag=imag/N;
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
cout << "Hello World!" << endl;
double real[8] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8};
double imag[8] = {0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0};
double realTwo1[8][8] = {{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8},
{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8},
{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8},
{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8},
{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8},
{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8},
{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8},
{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8}};
double realTwo[8][8]={{1,2,4,1,2,4,2,5},
{1,2,4,1,4,4,2,0},
{8,2,4,1,8,4,2,5},
{1,2,4,1,2,5,2,5},
{1,8,4,1,2,4,2,5},
{1,2,8,0,2,4,2,5},
{1,9,4,1,2,4,8,5},
{1,9,4,1,2,4,8,5}};
double imagTwo[8][8] = {{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},};
fit(real,imag,8,3,1);
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
cout<<real<<" "<<imag<<endl;
}
//cout<<imag[1];
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
fit(realTwo,imagTwo,8,3,1);
}
//转置数组
for (int j = 0; j < 8 ; j++)
{
for (int i = j; i < 8; i++)
{
double temprealTwo = 0.0;
temprealTwo = realTwo[j];
realTwo[j] = realTwo[j];
realTwo[j] = temprealTwo;
double tempimagTwo = 0.0;
tempimagTwo = imagTwo[j];
imagTwo[j] = imagTwo[j];
imagTwo[j] = tempimagTwo;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
fit(realTwo,imagTwo,8,3,1);
}
//转置数组
for (int j = 0; j < 8 ; j++)
{
for (int i = j; i < 8; i++)
{
double temprealTwo = 0.0;
temprealTwo = realTwo[j];
realTwo[j] = realTwo[j];
realTwo[j] = temprealTwo;
double tempimagTwo = 0.0;
tempimagTwo = imagTwo[j];
imagTwo[j] = imagTwo[j];
imagTwo[j] = tempimagTwo;
}
}
for (int j = 0; j < 8 ; j++)
{
for (int i = j; i < 8; i++)
{
cout<<realTwo[j]<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
|